Notes
Source: 📖 Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures using Python ch8.4
What is an adjacency matrix?
An adjacency matrix is a way of representing and implementing a graph as a two-dimensional matrix. Each row and column in the matrix represents a vertex in the graph, and the intersection of the vertex at row \(r\) and the vertex at column \(c\) represents an edge from \(r \rightarrow c\). If an edge exists, the intersection will contain a number which represents the weight of the existing edge. If no number is present, no edge exists from \(r\) to \(c\).
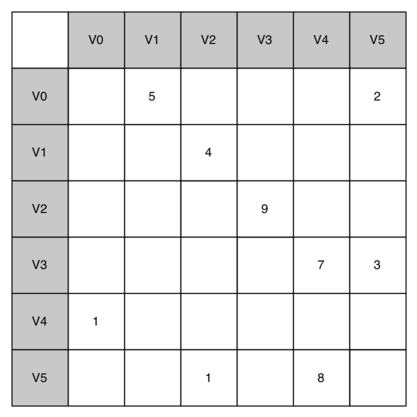
In the example adjacency matrix above, there is an edge with a weight of 5 from \(V0\) to \(V1\).
The problem with matrices is that they are inefficient for storing sparse data. As can be seen in the matrix above, in this example most cells are empty. Even though these cells don't contain any data they still need to be represented as part of the matrix nonetheless.
As the number of edges grows in relation to the number of vertices, a matrix becomes an increasingly better option. The maximum number of edges that can exist in a graph is when each vertex connects to every other vertex. For a graph with \(N\) vertices, this number is equal to \(N^2 - N\) meaning that every cell in the matrix would represent an existing edge, with the exception of the top-left to bottom-right diagonal as a vertex cannot have an edge connecting to itself.