Notes
Source: 📖 Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures using Python ch8.17
What is a topological sort algorithm?
Topological sort is an algorithm that can be used to turn a directed, acyclic graph into an ordered sequence. It utilises a depth first search algorithm to label all the vertices in a graph with a discovery and finish time, and then orders the vertices by descending finish times resulting in an ordered sequence.
But why is this required? There is a broad range of real world problems that can be represented as a graph. Of these, many are solved through a sequential series of steps. Graphs are a great way of representing problems with multiple steps and dependencies. Take a pancake recipe, for example. We first get all the ingredients, mix them into a bowl, heat a pan and pour portions of the mixture into the pan. We then wait for the pancake surface to bubble before turning them and waiting for them to finish cooking. On the side, we can also heat some syrup to pour over the top of the pancakes when the time comes to eat them. We could represent this recipe with the following graph.
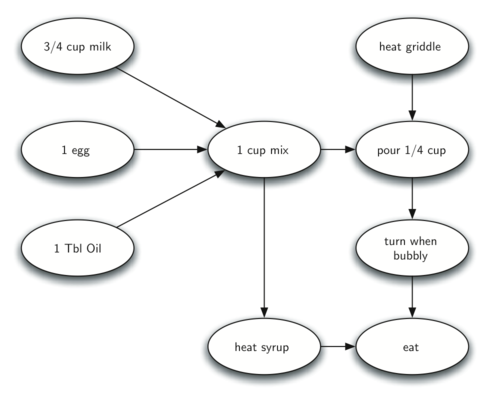
But this graph doesn't give any indication about where to begin. Running a topological sort algorithm on the graph will give us an ordered set of steps. As mentioned, first the algorithm runs a DFS on the graph. After the DFS algorithm has done its part, all the vertices in the graph will have been explored and labeled with discovery and finish times. These numbers can be seen below each vertex name below:
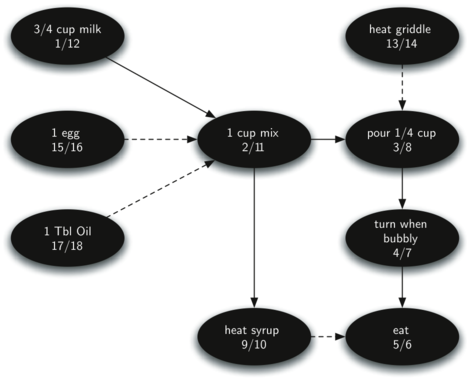
All that is left now is to put these vertices into a sorted sequence according to their associated finish times (the second number under the vertex name). This would result in the following sequence.
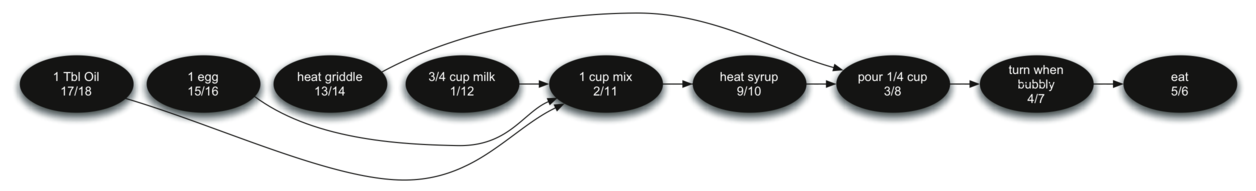
Now we have a series of ordered steps with no dependency issues.