Notes
Source: 📖 Problem Solving with Algorithms and Data Structures using Python 7.10
Date: 2021-12-28
Implementing a binary heap using a list
When implementing a binary heap, we do so using Complete binary trees. The nature of a complete binary tree means that it can be represented using a single list without any required nesting of sub-lists.
Imagining a complete binary tree, the order of its list implementation goes from top-to-bottom, left-to-right. In other words, we start with the root node, then its left child, then its right child. The same syntax is then propagated for each child node in order. The image below shows an example binary tree and its list representation (with index values shown):
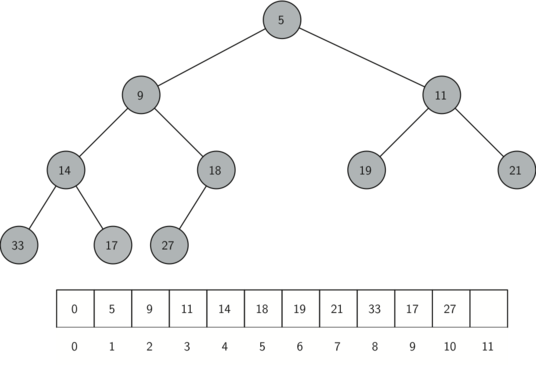
It should be noted that when representing a binary tree as a list, the first value is always assigned to 0. This allows us to use some simple mathematical formulas to find the child and parent of any given node in the list.
To find the left child of a node, we take its index value \(i\) and multiply it by 2.
$$list[i]left child = list[2i]$$
The right child can be found at index \(2i+1\).
$$list[i]right child = list[2i+1]$$
To find a node's parent, we use integer division:
$$list[i]parent = list[i//2]$$
Without occupying index 0 by default, these calculations would not work.